CONFERENCE PROCEEDING
Evaluation of the combined action of chlorsulfuron and dicamba
1
FBES F.F. Erisman Federal Scientific Center of Hygiene, Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing, Institute of Hygiene, Toxicology of Pesticides and Chemical Safety, Mytishchi, Russia
Publication date: 2024-11-26
Public Health Toxicol 2024;4(Supplement Supplement 2):A15
KEYWORDS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Weed resistance is one of the biggest problems in modern agriculture. Until now, the mechanism of the combined action of herbicides based on chlorsulfuron with preparations based on dicamba has been little studied, from the ingredients individually and in their total biological action.
Material and:
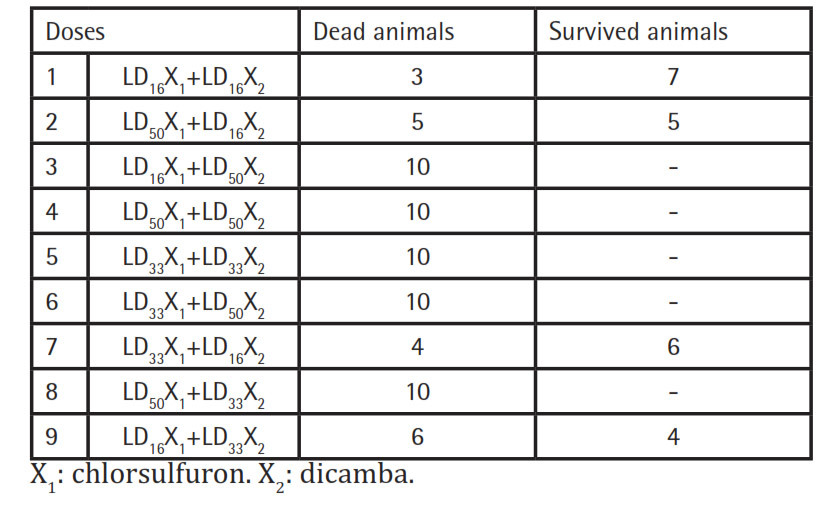
The study was performed on 138 outbred white male rats 250–300 g, randomly divided into 2 groups: the 1st group (48 rats) was subjected to a single oral priming to determine the effective (lethal) doses of each active substance under study, the 2nd group (90 rats) were subjected to a single oral inoculation with a combination of active ingredients under study. At the end of the experiment, the animals were euthanized in a CO2 box. To study the nature and the degree of interaction of these substances, the method of orthogonal planning of the experiment was applied using probabilistic values as the levels of factors (LD16, LD33, LD50) with an interval of their variation (LD17). The results of the studies were processed statistically.
Results:
The actions of chlorsulfuron and dicamba are interdependent; however, the effect of the interaction is less pronounced than the isolated interaction of factors. The isolated introduction of chlorsulfuron with increasing dose from LD33 to LD50 causes an increase in the death rate of animals by 3.3%, dicamba by 13.3%, and with their combined action by 11.7%.
Conclusions:
The nature of various combinations of chlorsulfuron and dicamba can be determined as an interdependent more additive effect.
Conflicts of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication of this article. The authors have no conflicts of interest to report in this work. Abstract was not submitted elsewhere and was first published here.
Funding:
This research received no external funding from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Weed resistance is one of the biggest problems in modern agriculture. Until now, the mechanism of the combined action of herbicides based on chlorsulfuron with preparations based on dicamba has been little studied, from the ingredients individually and in their total biological action.
Material and:
The study was performed on 138 outbred white male rats 250–300 g, randomly divided into 2 groups: the 1st group (48 rats) was subjected to a single oral priming to determine the effective (lethal) doses of each active substance under study, the 2nd group (90 rats) were subjected to a single oral inoculation with a combination of active ingredients under study. At the end of the experiment, the animals were euthanized in a CO2 box. To study the nature and the degree of interaction of these substances, the method of orthogonal planning of the experiment was applied using probabilistic values as the levels of factors (LD16, LD33, LD50) with an interval of their variation (LD17). The results of the studies were processed statistically.
Results:
The actions of chlorsulfuron and dicamba are interdependent; however, the effect of the interaction is less pronounced than the isolated interaction of factors. The isolated introduction of chlorsulfuron with increasing dose from LD33 to LD50 causes an increase in the death rate of animals by 3.3%, dicamba by 13.3%, and with their combined action by 11.7%.
Conclusions:
The nature of various combinations of chlorsulfuron and dicamba can be determined as an interdependent more additive effect.
Conflicts of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication of this article. The authors have no conflicts of interest to report in this work. Abstract was not submitted elsewhere and was first published here.
Funding:
This research received no external funding from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.